Vertigo is one of the common medical problems that in many cases has no specific cause. But when a person complains of this condition, doctors first guess the cause of severe vertigo due to a lesion in the inner ear. Vertigo is not a disease, but a symptom of various conditions that usually disturb the balance of the body. Most of the people who suffer from this disorder have reported feeling light in the head area and a large percentage of them have faced black eyes. In this case, you feel that the environment around you is rotating in a circle.
It must have happened to you that you suddenly lose your balance and feel that you or your surroundings are spinning. Vertigo occurs when you feel like you’re spinning, but you’re not. In most cases, this condition is associated with weakness and laxity of the body, which can be attributed to low blood sugar, extreme fatigue or dehydration. But some people experience head cycle disorder very severe or during sleep, which should be taken seriously.

Different types of Vertigo
This disorder usually has two main categories:
Peripheral: When the cause of severe vertigo is due to a problem in the inner ear, the rotational state occurs.
Central: This disorder occurs when there is a problem in the brain, especially the cerebellum, such as infection, brain tumor, traumatic brain injury or stroke.
It is good to know that vertigo will disappear on its own if it is not caused by a specific problem or underlying disease. But in some cases, failure to take timely action can cause irreparable damage.
Dizziness symptoms
This disorder is usually not considered a disease on its own, but a symptom of certain conditions in the body. In general, dizziness will be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting
- The lack of balance
- Tinnitus
- Headache
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
- Uncontrollable eye movement along the horizon, or vertically or rotating (Nystagmus)
Cause of dizziness
Some specific conditions and syndromes can cause severe and sudden dizziness. They include the following:
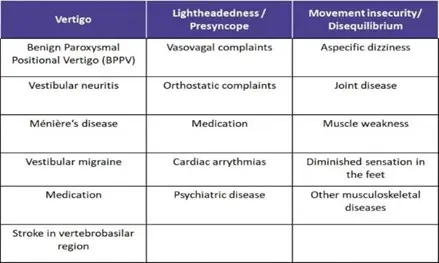
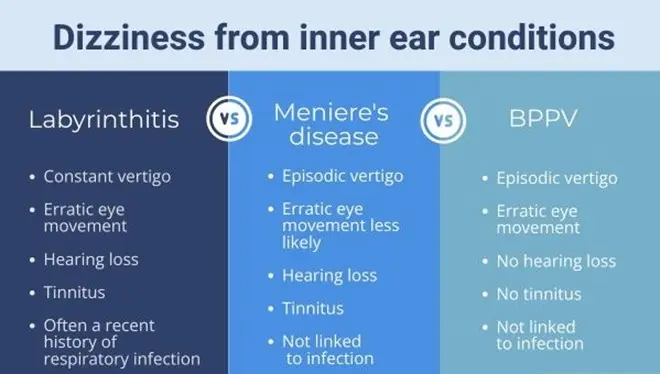
Benign Paroxysmal Vertigo (BPPV)
The most common cause of sudden vertigo is benign positional vertigo or BPPV, which occurs when a person changes the position of their head. This type of head rotation is usually experienced when a person is lying down, sitting or turning suddenly in bed.
Meniere’s disease
Accumulation of fluid in the inner ear caused by Meniere’s disease is the cause of vertigo attacks. Usually, this disease will not be cured, but the doctor will teach the patient the necessary training to manage its symptoms. Symptoms of tinnitus (ringing in the ears), hearing loss and ear fullness are annoying symptoms of Meniere’s disease.
Labyrinthitis
The inner ear or labyrinth has a vestibular nerve that is responsible for transmitting information about sound, head movement and its position to the brain. If the inner ear becomes inflamed due to infection, it is called Labyrinthitis. Symptoms of this disease are headache, earache, tinnitus, vision changes and hearing loss.
Vestibular neuritis
Another cause of severe headache is vestibular neuro-inflammation. Vestibular neuritis is similar to labyrinthitis, except that it does not cause hearing loss. Sudden dizziness, blurred vision and nausea are the most common symptoms of vestibular neuritis.
Cholesteatoma
This disease is a non-cancerous growth of the skin in the middle ear that is caused by frequent ear infections. Cholesteatoma is associated with severe dizziness, balance disturbance and hearing loss.
Other effective factors in creating head circumference
- Migraine headaches
- Stroke
- Head injury
- Long rest in bed
- Ear surgery
- Ear infection
- Leakage of inner ear fluid into the middle ear
- Decreased blood pressure while standing
- Muscle weakness
- Otosclerosis or abnormal bone growth in the middle ear
- Multiple sclerosis
- If you suddenly feel dizzy without a specific reason or situation, you should take it seriously.

What is the cause of dizziness in sleep?
If you wake up feeling dizzy, weak, and unsteady, it could indicate a specific illness or condition. Usually the cause of dizziness in sleep is caused by the following factors:
- Medicines: Some anti-depressants, blood pressure, allergy, anticonvulsants, sedatives and prostate medicines increase the possibility of headaches in sleep.
- Dehydration: not drinking enough fluids is one of the main causes of dizziness in sleep. Dehydration will cause the brain and body to not function properly, which results in headaches. Be sure to drink water a few hours before going to bed.
- Heart failure: This problem means not pumping blood properly to different parts of the body. As a result, a drop in blood pressure occurs and the body cannot tolerate it, which appears in a serious way, especially when sleeping and getting up from bed.
- Hypoglycemia: A drop in blood sugar causes various hormonal and chemical changes in the body, which should be considered as the cause of dizziness during sleep, especially in the early morning.
Persistent dizziness when waking up can indicate a disease or a specific condition in the body.
Vertigo diagnosis method
A neurologist or an otolaryngologist will first take a history from you during a physical examination about your period symptoms. They may also need other tests to confirm their diagnosis. You can see its test types in the following:
Head thrust test: While you are focused on a fixed target, the doctor moves your head in any direction.
Romberg test: to evaluate balance, eyes closed, feet together and hands at the sides.
The Fukuda-Unterberg test: asks you to stand there for 30 seconds with your eyes closed to check your inner ear and balance.
Dix-Hallpike test: To check eye movement, the patient goes from a sitting position to a lying position by being placed on the examination bed.
Vestibular test battery: to evaluate inner ear problems with spectacles.
CT Scan and MRI: imaging tests to diagnose vertigo-related disease
